Hair Loss Alopecia: Causes, Symptoms, and Regrowth Options
Table Of Content

If they suspect an autoimmune or skin condition, they might take a biopsy of the skin on your scalp. This involves carefully removing several small sections of skin for laboratory testing. Traction alopecia results from too much pressure and tension on the hair, often from wearing it in tight styles, like braids, ponytails, or buns.
Hair Loss in Women: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
The sooner you start treatment, the better the chances for hair regrowth. When it comes to effluvium—rapid hair shedding due to physical or emotional stress—treatments focus on finding the underlying cause. If a medication or disease is at the root, treatments focus on those. For anagen effluvium, caused by cancer treatment, there’s some evidence that cooling the scalp during chemotherapy may help preserve hair. Dietary factors and nutrition can also play a role in male hair loss.
What can doctors do?
However, the medication has still been used off-label for years to treat hair loss in women. More research is needed before definitive claims can be made regarding its effectiveness. And any medical conditions that lead to hair loss should be treated directly to address the condition, not just its symptoms. Stress causes a large number of hairs in the active hair growth (anagen) phase to abruptly enter the resting (telogen) phase. When the hairs reenter the growth phase, the hairs that had been suspended in the resting phase are suddenly released.
Why is my hair falling out? Learn the causes of hair loss
Perhaps one of the most common hormone-related causes for hair loss is a thyroid problem. Both too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism) and too little (hypothyroidism) can lead to hair loss. Treating the thyroid disorder can often reverse the hair loss. Sudden weight loss and very restrictive diets can also cause telogen effluvium. In men and women, such hair loss can accompany rapid weight loss following bariatric surgeries, such as gastric bypass. Though hair loss can’t always be reversed, knowing what’s at the root of hair loss is critical in managing it.
Chemotherapy and Medications
However, the cycle can be disrupted by the likes of aging and hormonal changes, such as menopause. As you age, some follicles no longer grow new hair, leading to a thinner look or bald patches. A dermatologist also can find the cause or causes and tell you what you can expect.

How can I prevent hair loss?
If you’ve been noticing more hairs on your pillow or hairbrush than normal, you may worry that you have hair loss. You could actually just be shedding more hairs than normal. It is intended for general informational purposes and is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Is hair loss contagious?
Hairstyles like cornrows, braids, or tight ponytails can cause it. Some signs of traction alopecia include hair loss in patches where the hair was pulled and shorter strands of hair near the forehead. Taking hormones can change hair growth all over your body. Masculinizing hormone therapy (taking testosterone) may cause hair loss within a year, and the effects aren't reversible if you stop hormone treatment. Hair growth naturally slows with age, so you may notice thinning.
Since there are many types of hair loss and many factors that can cause it, it’s important to understand who is at more risk. Certain health conditions raise your risk of both sudden hair loss (like telogen or anagen effluvium) and progressive hair loss (androgenetic alopecia). Female pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) is the most common cause of hair loss in women, but there are many other potential causes. As with medical conditions, physical changes that stress the body, especially if they cause hormonal changes, can lead to excessive hair shedding.
Why is my hair falling out? - USA TODAY
Why is my hair falling out?.
Posted: Wed, 18 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
What Causes Hair Loss in Teenagers, and How to Treat It
Many people who have plaque psoriasis develop psoriasis on their scalp at some point. A few months after giving birth, recovering from an illness, or having an operation, you may notice a lot more hairs in your brush or on your pillow. This can also happen after a stressful time in your life, such as a divorce or death of a loved one.
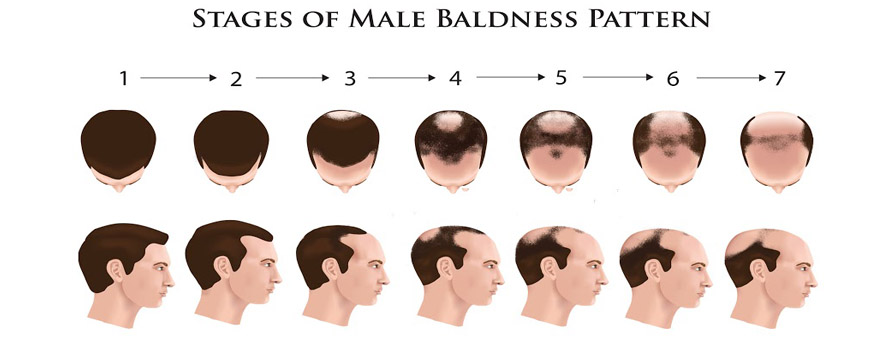
Many people who have hereditary hair loss continue to lose hair without treatment. A woman who inherits the genes for hereditary hair loss may notice gradual thinning. Men who have hereditary hair loss tend to develop a receding hairline or bald patch that begins in the center of the scalp. Hair loss can affect people differently depending on genetics, hormonal changes, or health conditions. Regardless of the cause, treatment to regrow hair is typically more effective if you catch hair loss early.
Before pursuing hair loss treatment, talk with your doctor about the cause of your hair loss and treatment options. Other causes, like genetic hair loss, have no known cure and will likely progress with time but can be slowed down with treatment. Some forms of hair loss are hereditary or caused by illness, so there’s no foolproof way to prevent clumps from falling out. Hair styling without damageMaking some simple changes to your hair care can help prevent hair breakage that can eventually cause hair loss.
Once the hair follicle is permanently damaged, hair can not grow back. The most common cause of male and female hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, or hereditary pattern balding. Androgenetic alopecia is genetic and is caused by a reaction to androgen and occurs after puberty.
You’ll probably notice a change several weeks or months after you stop. This usually isn't noticeable because new hair is growing in at the same time. Hair loss occurs when new hair doesn't replace the hair that has fallen out. Regularly coloring your hair or getting chemical hair treatments can damage your hair, and potentially lead to an increase in hair breakage. These treatments don’t usually affect your hair root, and your hair will likely grow back once you stop treatment.
On the whole, it’s important that you speak with your doctor about any symptoms you’re experiencing. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis, and select a personalized treatment that will help restore health to you hair and scalp. Anyone can have androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness). You may want to shift where hair grows (or doesn't) to reflect your affirmed gender. Female hair loss happens when a woman, or anyone who was identified as female at birth, loses more hair than normal.
The most common products contain an ingredient called minoxidil. This usually happens because of radiation treatment or chemotherapy. While it’s more prevalent in older adults, anyone can experience it, including children. If you’re not getting enough of one or more of these, you can have noticeable hair loss.
Comments
Post a Comment